Liquity Investment Thesis
User set interest rates, licensing fees, and real yield mechanics make Liquity V2 ($LQTY) an interesting asymmetric bet in DeFi.
Disclaimer: This piece was originally written in February 2025 and reflects information and opinions available at that time. While I’ve included a postscript to account for major updates since then, some figures or timelines may no longer be current. This is not financial advice. Always do your own research.
Liquity is a decentralized CDP platform and lending protocol that issues LUSD, a fully backed, stablecoin, through interest free loans using ETH as collateral on V1. And now with the launch of V2, supporting LSTs and introducing BOLD, a new stablecoin with user-set interest rates. By combining the best of V1 and improving on them in V2, Liquity is well positioned for significant market growth and remains underappreciated.
Market Cap: $134m FDV: $138m TVL: $437m
Holding Period: 3-6 MonthsExecutive Summary
Investment Thesis
Liquity V2 offers a compelling asymmetric upside by introducing user set interest rates, sustainable real yields, and multi collateral support. These innovations address V1’s limitations and position Liquity as a leading decentralized stablecoin and lending protocol. Its more capital efficient CDP mechanisms allow users to become interest makers rather than takers, creating a foundational DeFi primitive with significant efficiency gains. V2’s business license model addresses V1’s forking issue, ensuring direct value accrual to Liquity and a sustainable growth path. While LUSD remains robust and uncensorable, V2 introduces BOLD to fuel future adoption. V1’s fixed fees struggled in high interest environments, but V2’s dynamic rates adapt to market conditions, enhancing resilience and efficiency. With licensed forks reinforcing the ecosystem and BOLD driving stablecoin growth, V2 is poised to become Liquity’s primary engine for Total Value Locked (TVL) expansion and long term value accrual. Given V2's innovative features, sustainable tokenomics, and enhanced capital efficiency, Liquity is well positioned to capture significant market share in the decentralized lending space.
Trade Idea
I propose a long position in LQTY ahead of V2’s launch, driven by the anticipated adoption of BOLD as a leading yield bearing stablecoin. As BOLD gains traction, it will fuel protocol revenues and expand Liquity’s TVL. The upcoming wave of licensed V2 forks will further amplify value accrual, directly supporting LQTY’s price growth over the next 3-6 months.
Primer and Liquity V1
Liquity is a decentralized finance (DeFi) protocol that revolutionized the stablecoin and lending sectors by introducing LUSD, a fully backed stablecoin issued through interest free loans using ETH as collateral. Unlike traditional lending platforms like MakerDAO, which impose recurring interest rates, Liquity’s model allows for a one time borrowing fee between 0.5% and 5%, providing borrowers with predictable and transparent costs. This approach not only enhances accessibility but also reduces financial commitments for users, making Liquity an attractive option for capital efficient lending.
The core of Liquity’s value proposition lies in its commitment to decentralization and autonomy. LUSD operates without reliance on centralized entities or human governance, addressing a growing demand for censorship resistant and stable digital assets. The protocol’s immutable architecture ensures resilience against market volatility and regulatory pressures, distinguishing it from centralized stablecoins like USDT and USDC, which face risks of censorship and regulatory scrutiny.
Key Mechanisms of Liquity V1
Price Stability Mechanism: LUSD maintains its peg to the US dollar through a robust redemption system where 1 LUSD can always be exchanged for $1 worth of ETH. This mechanism incentivizes arbitrage, ensuring that LUSD remains stable even during market fluctuations.
Liquidation Mechanism: To safeguard against excessive debt, Liquity employs a unique instant liquidation process triggered when a borrower’s collateral ratio falls below 150%. This process eliminates the need for traditional auctions, enhancing system efficiency.
Supply Control Mechanism: Liquity’s design minimizes the need for active management, reducing collateral demands while maintaining stability.
Successes and Challenges of Liquity V1
Liquity V1 found considerable success in establishing itself as a pioneer of decentralized, interest free lending. Its model attracted a dedicated user base seeking transparent and predictable borrowing costs and a stablecoin backed purely by ETH. The protocol’s ability to maintain stability without relying on real world assets demonstrated the robustness of its design, even during periods of market volatility. Additionally, its immutable nature and censorship resistant architecture solidified Liquity’s reputation as one of the most decentralized stablecoin platforms in DeFi.
However, Liquity V1 faced key challenges. In high interest environments, the protocol struggled to maintain competitiveness against flexible, yield bearing stablecoins offering more attractive returns. The fixed fee model, while predictable, limited its appeal under dynamic market conditions. Moreover, the proliferation of over 35 forks diluted the ecosystem’s value, as these forks failed to contribute to the growth or value accrual of LQTY, Liquity's native token. This exposed a critical flaw in Liquity’s tokenomics, where value did not sufficiently flow back to token holders, undermining long term incentives.
Another significant issue arose from the redemption mechanism. In V1, borrowers could avoid redemptions by increasing their loan to value ratios, leading to an uneven risk distribution and reduced capital efficiency during volatile markets. This meant that when redemptions were triggered, positions were sorted by loan to value, starting from the bottom. Borrowers who manipulated their ratios could effectively shield themselves from redemptions, undermining the fairness and robustness of the system. This flaw became particularly problematic during market downturns when LUSD fell below its peg, leading to aggressive redemptions that hurt user confidence and capital efficiency.
These successes and shortcomings set the stage for Liquity V2, designed to address the limitations of V1 while building on its core strengths. V2 introduces a more market driven redemption mechanism where loan positions are sorted by user set interest rates. Positions with the lowest interest rates are redeemed first, incentivizing borrowers to balance risk and reward. This innovation aligns user and fork behavior with the protocol’s health, ensuring more sustainable and equitable outcomes across varying market conditions.
Market Context and Total Addressable Market (TAM)
The stablecoin market has experienced explosive growth, reaching over $217B , with projections suggesting a rise to $2.8T by 2028. However, centralized solutions dominate with USDT & USDC with over 90% of stablecoin holdings. This presents a significant opportunity for decentralized stablecoins like LUSD to capture market share.
Centralized stablecoins like USDT and USDC lack the flexibility to implement native revenue sharing mechanisms due to their reliance on centralized custodians and regulatory constraints. This contrasts sharply with decentralized protocols like Liquity, where stablecoins such as LUSD and the upcoming BOLD allow revenue from borrowing fees to flow directly back to users and the ecosystem.
Liquity V2
Liquity V2 builds upon V1 by introducing new novel innovations that enhance its functionality. Unlike V1, which relied solely on ETH as collateral and had fixed borrowing fees, V2 supports Liquid Staked Derivatives (LSDs) like Lido’s wstETH and Rocketpool’s rETH. This not only diversifies collateral options but also allows users to earn yield on their collateral while borrowing, addressing a major limitation of V1.
The introduction of BOLD, a new stablecoin, represents a pivotal shift in Liquity’s model. BOLD features user set interest rates ranging from 0.5% to 25% annually, giving borrowers unprecedented control over their loan costs and redemption risks. Borrowers can adjust their interest rates at any time, paying a nominal fee equivalent to seven days of interest upon adjustment. This dynamic replaces the static one time fee of V1, making Liquity V2 more adaptable to varying market conditions.
In V1, redemptions were sorted based on loan-to-value (LTV) ratios, which often penalized users with higher leverage. In V2, the redemption mechanism prioritizes loans with the lowest interest rates. This shift means borrowers who set lower rates to minimize borrowing costs face a higher risk of early redemption, while those who pay higher rates can secure their positions longer. This mechanism aligns user incentives with risk tolerance and further enhances capital efficiency and user autonomy.
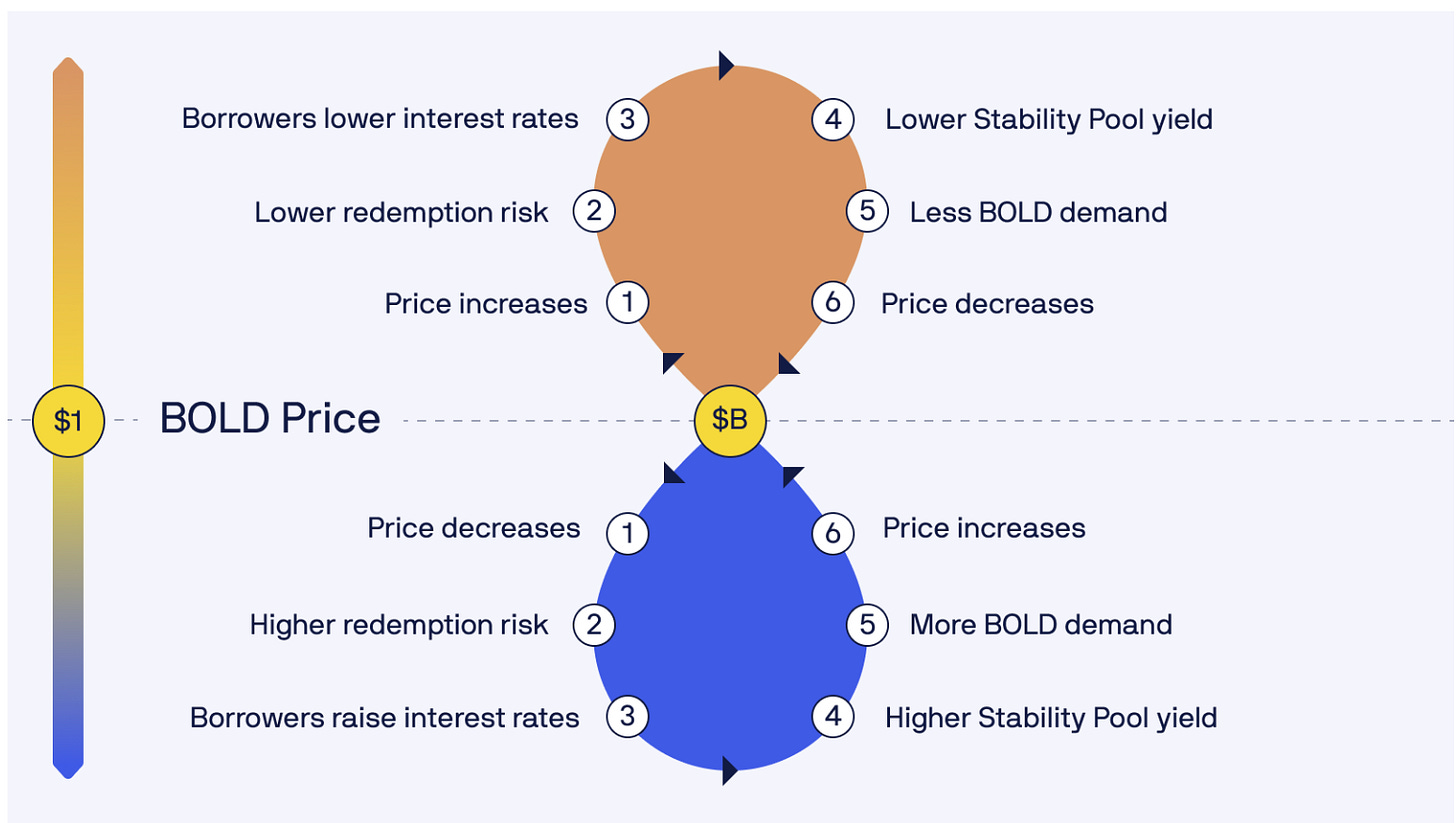
BOLD Peg
BOLD’s peg stability relies on this dynamic interest rate model. When BOLD trades below $1, redemptions are triggered, starting with the Troves paying the lowest interest rates. Borrowers then have an incentive to increase their interest rates to avoid being redeemed, which raises yields for BOLD holders and restores demand, pulling the stablecoin back to its peg. Conversely, when BOLD trades above $1, borrowers lower their rates, reducing yields and prompting holders to sell, nudging the price back to parity. This self correcting mechanism is entirely market driven, requiring no external governance interventions.
Additionally, Liquity V2 introduces a delegation feature, allowing users to delegate interest rate management to third parties or automated strategies. This enables passive management of borrowing positions while maintaining competitive rates and minimizing redemption risks. Delegates can only adjust interest rates within predefined parameters, ensuring borrower security.
Liquity V2 also removes the Recovery Mode present in V1, which was designed to protect against under collateralization during volatile markets. In its place, V2 implements a stricter collateral shutdown mechanism, activating if the total collateral ratio falls below 110% for ETH and 120% for LSDs. This approach ensures capital efficiency while safeguarding the protocol’s solvency.
Catalysts & Tailwinds For Liquity
Liquity V2 introduces a transformative licensing model designed to address V1's most significant flaw: uncontrolled forks. While V1’s 35+ forks showcased its popularity, they diluted value without channeling benefits back to LQTY holders. The introduction of a Licensed Fork Model safeguards protocol value. The strong developer interest, evidenced by 15 teams seeking to fork the protocol, demonstrates significant market demand that appears not yet reflected in current valuations. This interest is particularly noteworthy given V2's recent launch, which has already attracted $72M in TVL on a single blockchain network in less than a week.
How the Licensed Fork Model Works
Business License Framework: V2’s code is under a Business Source License (BUSL), requiring teams to license any forks until September 2027, ensuring direct value accrual to Liquity through fees.
Independent Operation: These forks operate independently from Liquity, with separate governance and risk frameworks. Liquity AG holds no operational or financial risk from these forks, ensuring the core protocol remains insulated from external failures.
Expansion Across Ecosystems: Over 15 V2 friendly forks will launch on chains like Arbitrum, Base, Berachain, and more, driving TVL growth and reinforcing BOLD as a DeFi staple.
Value Accrual Mechanisms & Competitor Outlook
Licensed Fork Revenue: Liquity V2 is protected under a Business Source License (BUSL), meaning all forks must obtain a license through Liquity AG to deploy. These forks contribute back to Liquity in two core ways:
A portion of protocol revenue from each fork is paid back to Liquity. While I couldn’t find the exact revenue share for every fork, it does establish a recurring income stream directly tied to ecosystem usage. That said, some concrete numbers here from the team would add a lot more color.
4% of the fork’s token supply is allocated to the Liquity ecosystem, primarily to LQTY stakers and BOLD stability pool participants giving native holders exposure to the growth of new forks.
Protocol Incentivized Liquidity (PIL): 25% of protocol revenues from forks will be directed back to the Liquity ecosystem, supporting liquidity pools and further driving LQTY demand.
Bootstrapping Fork Adoption: Forking teams incentivize early BOLD holders to provide liquidity in new ecosystems, which fosters adoption and stabilizes the stablecoin. This creates a self reinforcing cycle where rising BOLD demand increases Liquity’s revenues, boosts yields, and attracts more users. Notably, 75% of rewards go to BOLD stability depositors.
No Emissions Left: With no emissions left to dilute LQTY’s value, the protocol now relies on organic growth and revenue generation. This positions LQTY as a scarce asset, with its value directly tied to protocol activity and staking rewards.
Poor Competitor Performance
MakerDAO has struggled to grow its DAI supply, relying heavily on centralized collateral like USDC and facing governance centralization issues. As I’ll cover in the next section, MakerDAO is also experiencing negative annualized profits. Other competitors, like USDe, have performed well recently but face scaling challenges due to their reliance on ETH and arbitrage opportunities, which are already diminishing. (4% USDe rates as of June 29, 2025)
Competitor Analysis & Valuation: MakerDAO/SKY Vs Liquity
The closest competitor and likely the best comparison for Liquity is MakerDAO, one of the largest decentralized stablecoin issuers and a prominent CDP based borrowing and lending protocols. Both platforms operate in the decentralized stablecoin sector, making MakerDAO Liquity’s primary rival for market share. However, this market remains relatively small, with decentralized stablecoins representing only about $17B of the total $217B stablecoin market, the majority of which is dominated by centralized issuers like USDT and USDC. As Liquity seeks to expand its presence, outperforming MakerDAO in efficiency, governance, and revenue generation will be key to capturing a larger share of this growing sector.
That said, valuing Liquity poses some challenges. Liquity V1 is still operational, with steady revenue, but it represents an older model that struggled with scalability and fork related issues. The focus now is on Liquity V2, which introduces a more sustainable, efficient framework. However, since V2 launched just a week ago, it’s still early to draw firm conclusions. The initial growth has been promising, but the protocol is clearly in a rebuild phase.
This section will analyze both protocols using key metrics such as TVL to Market Cap Ratio, Collateralization Ratio, and Revenue per Stablecoin Issued to highlight Liquity’s competitiveness.
TVL to Market Cap Ratio
The TVL to Market Cap ratio is a common DeFi valuation metric, although I don’t believe it tells us much on its own. As it doesn’t capture key factors like profitability, revenue generation, or capital efficiency. I think when combined with other metrics like revenue per stablecoin issued or collateralization ratios it becomes a helpful tool for quick comparisons and a general valuation check. It’s not the most comprehensive metric, but it’s useful for getting a rough sense of how protocols are valued relative to the assets they manage.
Liquity’s combined TVL/MC ratio of 2.8 suggests stronger capital deployment relative to its market valuation compared to MakerDAO’s 0.17. This indicates that Liquity manages more assets per unit of market cap, reflecting potential undervaluation or more efficient capital use. However, with Liquity V2 in its infancy and the protocol still in a rebuild phase, it’s too early to make definitive judgments. On the other hand, MakerDAO’s lower ratio may seem attractive, but it doesn’t account for underlying inefficiencies or performance issues, making this metric useful only when considered alongside other metrics we will discuss.
Collateralization Ratios & Capital Efficiency
Collateralization ratios play a critical role in determining a protocol’s capital efficiency and borrowing attractiveness. Higher collateral requirements lock up more capital, limiting borrowing flexibility, while lower ratios allow for greater capital utility and more accessible borrowing.
Maker DAO Ratio
Liquity Ratio
MakerDAO operates with a 411% collateralization ratio, meaning users must lock up over four times the amount they wish to borrow. This excessive capital lock up inflates MakerDAO’s TVL without driving corresponding borrowing activity or revenue, making the platform less efficient for users. This inefficiency is reflected in MakerDAO’s low TVL/MC ratio of 0.17, indicating that despite a large asset base, the protocol struggles to deploy capital productively. In contrast, Liquity boasts a 197.7% collateralization ratio, allowing users to borrow more with less collateral. This increased capital efficiency makes the protocol more attractive to borrowers, enabling higher utilization of locked assets. As a result, Liquity’s TVL/MC ratio of 2.8 starts to make a lot more sense as it reflects stronger capital deployment relative to market valuation.
Revenue Per Stablecoin Issued
When comparing revenue generation efficiency, Liquity V2 stands out. Despite its smaller stablecoin supply of $29 million BOLD, Liquity V2 generates an estimated $5 million in annualized revenue, translating to $0.172 revenue per $1 issued. This is more than double MakerDAO’s $0.077 per $1 issued, highlighting Liquity V2’s superior revenue efficiency.
Liquity V1, on the other hand, shows much lower revenue efficiency at $0.016 per $1 issued, reflecting the challenges and inefficiencies of its older model. However, when combining Liquity V1 and V2, the total revenue per $1 issued reaches $0.068, closing the gap with MakerDAO despite Liquity’s significantly smaller stablecoin footprint. This comparison underscores Liquity V2’s strong potential to outcompete MakerDAO in terms of revenue efficiency as it scales.
MakerDAOs Profitability Issues (Feb 2)
Looking at the graph, it's clear that MakerDAO's annualized revenues have taken a big hit, showing just how much the protocol has been struggling. The recent rebrand to SKY hasn't really moved the needle, and even though fee income has stayed steady, some questionable governance choices have driven annualized profits down to negative $11m. One major misstep was setting the DSR rate at 9% without a solid plan, which hurt profitability without attracting more users.
Slow governance and inefficiency have also allowed many poor performing vaults to remain active, draining resources at the cost of MakerDAO holders. In contrast, Liquity takes a more straightforward approach by funneling all revenue directly to BOLD and LQTY holders. This creates stronger incentives for liquidity and offers more sustainable, real yield rates. Moreover, DAI supply has been stuck around $6 billion for a while now, with little to no growth. On top of that, MakerDAO's attempts to branch out into equities and RWAs haven't paid off, leading to missed opportunities and financial losses. All of this points to deeper issues with how the protocol is managed and how capital is being allocated.
Conclusion
Comparing Liquity and MakerDAO across TVL to Market Cap ratio, collateralization ratios, and revenue per stablecoin issued shows Liquity’s stronger capital efficiency and revenue potential. Liquity V2’s lower collateral requirements and higher revenue per $1 issued highlight more productive capital use compared to MakerDAO’s inefficient structure. While Liquity V1 reflects past struggles, V2’s early performance shows strong potential for growth. MakerDAO’s high collateralization ratio, negative profits, and slow governance limit its scalability. Liquity’s focus on efficiency and sustainable revenue position it to capture more market share in the decentralized stablecoin sector.
Postscript: What’s Happened Since February
Since writing this memo back in February, Liquity hit a bit of a bump. A bug was discovered in the V2 contracts, and the team made the decision to temporarily shut down and redeploy V2 with updated contracts. No user funds were affected throughout the process.
A lot of the expected forks still haven’t gone live and adoption has been slower than I hoped. That said, I still think the fundamentals are strong. The BOLD mechanism, user set interest rates, and the new licensing model are all well thought out. Value should start to accrue to LQTY holders as these forks spin up. It won’t happen overnight, but I see it as a slow, steady build. If it plays out the way I expect, the flywheel from fee sharing, fork airdrops, and stablecoin growth could end up being pretty powerful.